Honey is best known as a healthier alternative to traditional sweeteners such as sugar (honey vs sugar). In fact, when you mention honey, for 4 in 5 people, this is what comes to mind. However, honey is much more than that - in ancient times dating as far back as 3500 BC it was known primarily for its medicinal uses.
What is honey
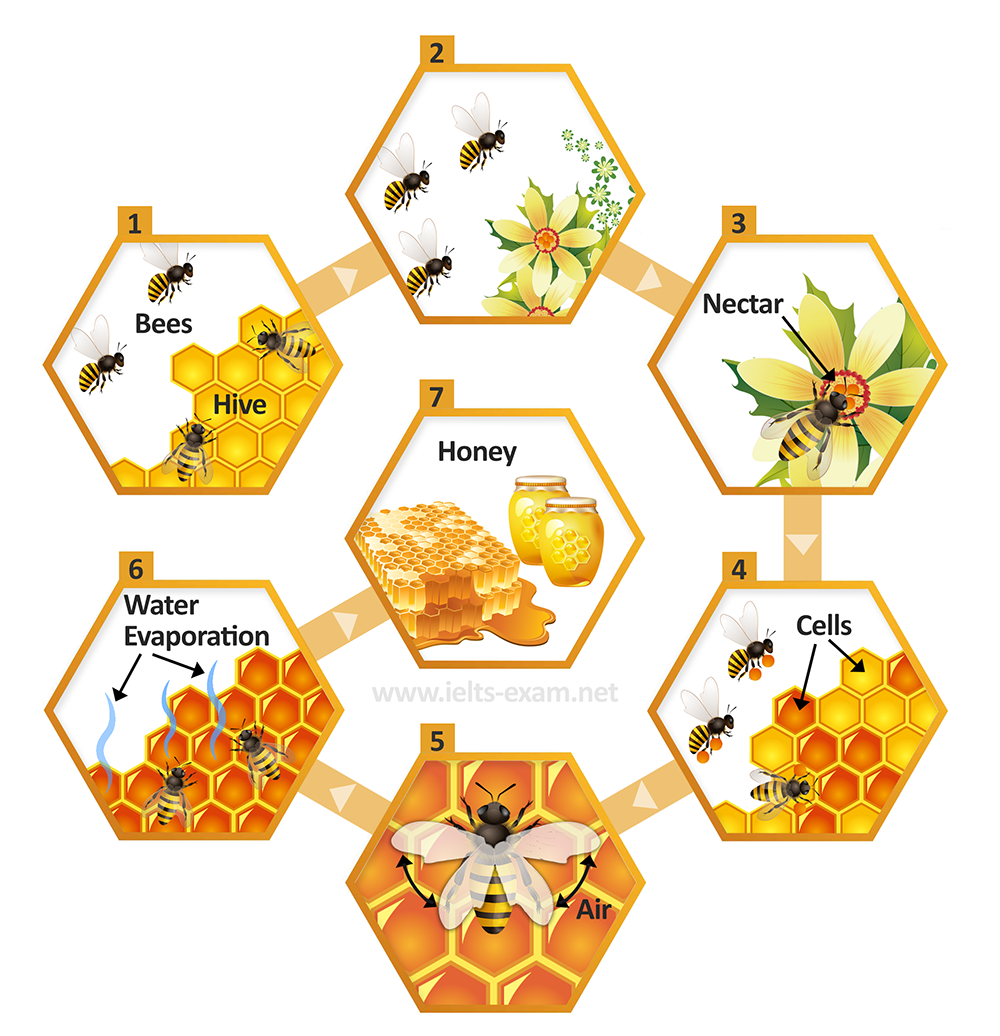
In simple terms, honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by bees. Bees produce honey by gathering and refining plants' sugary secretions, otherwise known as nectar. The conversion takes place within individual bees, through regurgitation and enzymatic activity, after which it is stored in honeycombs, where it is concentrated until it becomes thick and viscous through water evaporation. Honey is mainly composed of the sugars, fructose and sucrose along with other compounds such as, minerals, vitamins, etc.
History of honey
Honey has a long and varied history, it has been around for as far back as we can trace, which makes it hard to pinpoint when it was discovered. Our first record of organized beekeeping (also known as apiculture) dates back to ancient Egypt, circa 3,500 BCE, and fossils of honey bees date back about 150 million years. In the early 1920’s, cave paintings were discovered in the Cuevas de la Araña of Valencia, Spain that clearly depict a human figure collecting honey directly from a hive. Due to its sweetness as a food and medicinal properties, honey has been revered amongst multiple cultures for more than a millennium. The ancient Egyptians, Greeks and Romans not only used it for cooking but as a gift to the gods. The history of honey as medicine can be traced back to the Greeks, who considered honey as a healing medicine. It was also used as an ingredient in embalming fluid in ancient Egypt. Honey has been mentioned in various ancient and religious texts, mostly for its medicinal uses.
To read more: History of honey
Medicinal honey: The medicinal pot of gold
Honey has been used as a medical treatment since Antiquity. Hippocrates, the classical Greek philosopher known as the ‘father of modern medicine’, noted the benefits of honey and used it in various formulations for treating various illnesses, injuries, and other health issues. The ancient Indian Vedic civilization that developed Ayurvedic medicine considered “Madhu”, honey, as one of the most remarkable gifts of nature to mankind, and used it to treat a wide variety of ailments. Ancient Chinese, Roman, and Assyrian medicine employed honey for the treatment of flesh wounds and diseases of the gut, among other uses. But what makes honey medicinal?
Honey's medicinal nature can be attributed to its anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antioxidant properties. These properties mean that it can help fend off the spread of viral and bacterial infection in your body – maintaining your cardiovascular, metabolic, digestive, neurological, and dermatological health. However, although honey is lauded as medicine, not all varieties are effective medicines. So what kind of honey is medicinal? Manuka honey is considered the most medicinal. Though, any raw, unprocessed honey will do.
Health benefits of honey
- Promotes burn and wound healing: There is a historical precedent for the use of topical honey treatment for wound and burn healing. The practice is still common today. It aids in maintaining a moist wound condition, and its high viscosity helps to provide a protective barrier to prevent infection. Its immunomodulatory property is also relevant to wound repair.
- Cough relief: According to folklore or a 2012 study published in the Journal of Pediatrics, just two teaspoons of honey can help cure a persistent cough. Thanks to its antimicrobial properties, honey not only soothes the throat but also kills certain bacteria which cause the infection.
- Immune booster: Honey is a powerhouse of antioxidants, which are very effective for the removal of free radicals from the body. Furthermore, its antioxidant and antibacterial properties help improve the digestive system and boost immunity.
- Heart diseases: Honey is known to help with cardiovascular diseases and also lowering cholesterol levels. According to Dr. Manoj K. Ahuja, Sukhda Hospital, consumption of natural honey increases polyphonic antioxidants in the blood which helps prevent heart diseases.
- Energy booster: About 80% of honey is made up of glucose and fructose. The glucose in honey is absorbed by the body quickly, giving an immediate energy boost, while the fructose provides sustained energy since it is absorbed more slowly.
- Skincare: Honey's high antioxidant and healing properties lend it the ability to soften, brighten, nourish, and clarify the skin. It is commonly used in skincare products for, moisturizing, anti-ageing, anti-acne, sunburn, blemishes, and hyperpigmentation.
- Haircare: Honey has both emollient and humectant properties, making it a great hair moisturizer. Emollients smooth the hair follicles, adding shine to dull hair and humectants bond with water molecules, adding moisture to dry strands. it also contains plenty of vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and antioxidants which aid with hair growth and conditioning.
- Sexual health: In 500 BC the Greek philosopher and father of modern medicine ¨Hippocrates¨ prescribed it to increase sexual vigor. Furthermore, recent research has found honey to increase testosterone which boosts sex drive as well as sperm production, count, and motility.
Fun fact: Did you know that in 400 BCE, when Greek soldiers tried to usurp the Persian throne, Persian generals defeated the Greeks by feeding local honeybees toxic rhododendron flowers, which in turn poisoned the honey supply of the Greek army?

Post a Comment